[ BLE 智能手环 ] [ 2 ] OSAL层工作原理
OSAL 程序启动流程
main 函数
/**************************************************************************************************
* @fn main
*
* @brief Start of application.
*
* @param none
*
* @return none
**************************************************************************************************
*/
// 任何8051单片机c程序, 都是由 main 函数开始的,
// 我们拿到一份代码,首先需要找到main函数
int main(void)
{
/* Initialize hardware */
HAL_BOARD_INIT(); //初始化时钟稳定时钟等等
// Initialize board I/O
//冷启动,关闭了led灯与中断, 以便接下来的各种初始化不受干扰
InitBoard( OB_COLD );
/* Initialze the HAL driver */
HalDriverInit(); //各种驱动的初始化、如按键、lcd、adc、usb、uart等
/* Initialize NV system */
//snv 内部用于保存配对数据或你的用户自定义数据的一段flash,4kB空间
osal_snv_init();
/* Initialize LL */
/* Initialize the operating system */
//oasl 操作系统初始化, 包含内存分配、消息队列、定时器、电源管理和任务等
osal_init_system();
/* Enable interrupts */
HAL_ENABLE_INTERRUPTS();// 开启全局中断
// Final board initialization
InitBoard( OB_READY ); //设置标志标示系统初始化完毕
#if defined ( POWER_SAVING )
// 如果你使能了低功耗, 就启动低功耗模式,
osal_pwrmgr_device( PWRMGR_BATTERY );
#endif
/*
低功耗部分
1.如何总是在PM1
osal_pwrmgr_device( PWRMGR_ALWAYS_ON );
2.如何进入PM2
osal_pwrmgr_device( PWRMGR_BATTERY );在空闲的时候就会进入到PM2模式
3.如何进入PM3
存在连接就断开连接,存在广播就停掉广播,并确认自己创建的所有定时任务都已关闭,
则系统应该就会进入PM3模式,只能进行外部中断唤醒
*/
/* Start OSAL */
osal_start_system(); // No Return from here
/* osal 操作系统启动,实际上是一个大循环,只是检查相对应的标志位,
就指定相对应的任务,看到这里,同学们应该往哪里看呢?其实,这已经是尽头了?那么我们的应用程序是在哪里写的呢
其实是在上面的 上面的函数 osal_init_system 里就初始化了,现在回过头去看看
osal_init_system 这个函数内部就知道了
*/
return 0;
}
osal_init_system() 该函数执行 app 初始化,以及启动事件函数执行。
void osal_start_system( void )
{
#if !defined ( ZBIT ) && !defined ( UBIT )
for(;;) // Forever Loop
#endif
{
osal_run_system();
}
}
osal 操作系统启动,实际是一个大循环。
/*********************************************************************
* @fn osal_run_system
*
* @brief
*
* This function will make one pass through the OSAL taskEvents table
* and call the task_event_processor() function for the first task that
* is found with at least one event pending. If there are no pending
* events (all tasks), this function puts the processor into Sleep.
*
* @param void
*
* @return none
*/
void osal_run_system( void )
{
uint8 idx = 0;
#ifndef HAL_BOARD_CC2538
osalTimeUpdate();
#endif
Hal_ProcessPoll(); //查询数据,比如串口数据,usb数据等
do { // 训环寻找是否有事件,有事件的话,就立马退出,app应用优先级最低
if (tasksEvents[idx]) // Task is highest priority that is ready.
{
break;
}
} while (++idx < tasksCnt);
if (idx < tasksCnt)// 找到了事件
{
uint16 events;
halIntState_t intState;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState); // 关闭中断
events = tasksEvents[idx]; //读取该任务的事件(事件可能不止1个)
tasksEvents[idx] = 0; // 清除时间记录,在执行任务处理函数期间有可置上新事件
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState); // 开启中断
activeTaskID = idx;
events = (tasksArr[idx])( idx, events );// tasksArr 是任务处理函数指针
activeTaskID = TASK_NO_TASK;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);// 关闭中断
tasksEvents[idx] |= events; // Add back unprocessed events to the current task.
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);// 开启中断
}
#if defined( POWER_SAVING )
else // Complete pass through all task events with no activity?
{ // 系统睡眠, 以便达到低功耗的目的
osal_pwrmgr_powerconserve(); // Put the processor/system into sleep
}
#endif
/* Yield in case cooperative scheduling is being used. */
#if defined (configUSE_PREEMPTION) && (configUSE_PREEMPTION == 0)
{
osal_task_yield();
}
#endif
}
tasksEvents 是个指针,在函数 osalInitTasks 中开辟了与任务处理函数个数一样多的 uint16 型数据(16位),其定义为:
/*
* Event handler function prototype
*/
typedef unsigned short (*pTaskEventHandlerFn)( unsigned char task_id, unsigned short event );
第一个形参 task_id 是任务 id,
第二个形参 events 是事件的意思,其被定义为 16 位,最多只能有 16 个事件,对单片机来说足够,如果需要更多,完全可以在 app 中通过自定义一个内部变量来实现分岔。
/*******************************************************************************
* @fn LL_ProcessEvent
*
* @brief This is the Link Layer process event handler called by OSAL.
*
* input parameters
*
* @param taskId - Task identifier assigned by OSAL.
* events - Event flags to be processed by this task.
*
* output parameters
*
* @param None.
*
* @return Unprocessed event flags.
*/
extern uint16 LL_ProcessEvent( uint8 task_id, uint16 events );
以下两个函数提供设置事件与清除事件功能:
uint8 osal_set_event( uint8 task_id, uint16 event_flag );
uint8 osal_clear_event( uint8 task_id, uint16 event_flag );
从上面任务数组可以看到,整个协议栈里有 11 个任务,数字越小的任务,优先级越高。
// The order in this table must be identical to the task initialization calls below in osalInitTask.
// 这个表相当重要, 都是定义了各个任务的事件执行函数,可以理解成回调函数,或事件执行函数
const pTaskEventHandlerFn tasksArr[] =
{
LL_ProcessEvent, // task 0
Hal_ProcessEvent, // task 1
HCI_ProcessEvent, // task 2
#if defined ( OSAL_CBTIMER_NUM_TASKS )
OSAL_CBTIMER_PROCESS_EVENT( osal_CbTimerProcessEvent ), // task 3
#endif
L2CAP_ProcessEvent, // task 4
GAP_ProcessEvent, // task 5
GATT_ProcessEvent, // task 6
SM_ProcessEvent, // task 7
GAPRole_ProcessEvent, // task 8
GAPBondMgr_ProcessEvent, // task 9
GATTServApp_ProcessEvent, // task 10
SimpleBLETest_ProcessEvent // task 11
// 这个是我们的应用程序的事件处理函数,在该函数内编写代码,可以处理按键、数据读写返回状态等。
};
下面是应用程序初始化代码,这已经实现多任务,而每一个任务中又实现最大16个事件的框架,除了在应用程序中实现任务初始化和任务处理函数,还有处理函数是以回调函数的形式出现。
/*********************************************************************
* @fn osalInitTasks
*
* @brief This function invokes the initialization function for each task.
*
* @param void
*
* @return none
*/
/*
可以看到在這個數組的定義中,每個成員都是任務的執行函數,按照任務的優先級排序,並且在osalInitTasks中初始化的時候,我們可以看到每個任務都有一個對應的初始化函數并且傳遞了一個taskID,此ID從0開始自增,這裏有一點非常重要,初始化的順序和任務數組的定義順序是一樣的,這就保證了我們給任務發生消息或事件時能夠準確的傳遞到相應的任務處理函數。
*/
void osalInitTasks( void )
{
uint8 taskID = 0;
// 分配任务事件空间,这里采用动态的方法来做,比较方便在tasksArr而代码修改少
tasksEvents = (uint16 *)osal_mem_alloc( sizeof( uint16 ) * tasksCnt);
osal_memset( tasksEvents, 0, (sizeof( uint16 ) * tasksCnt));
/* LL Task */
LL_Init( taskID++ );
/* Hal Task */
Hal_Init( taskID++ );
/* HCI Task */
HCI_Init( taskID++ );
#if defined ( OSAL_CBTIMER_NUM_TASKS )
/* Callback Timer Tasks */
osal_CbTimerInit( taskID );
taskID += OSAL_CBTIMER_NUM_TASKS;
#endif
/* L2CAP Task */
L2CAP_Init( taskID++ );
/* GAP Task */
GAP_Init( taskID++ );
/* GATT Task */
GATT_Init( taskID++ );
/* SM Task */
SM_Init( taskID++ );
/* Profiles */
GAPRole_Init( taskID++ ); // 角色初始化
GAPBondMgr_Init( taskID++ );
GATTServApp_Init( taskID++ );
/* Application */
SimpleBLETest_Init( taskID ); //这个就是我们的应用程序初始化
}
/*********************************************************************
* PUBLIC FUNCTIONS
*/
/*********************************************************************
* @fn SimpleBLETest_Init
*
* @brief Initialization function for the Simple BLE Peripheral App Task.
* This is called during initialization and should contain
* any application specific initialization (ie. hardware
* initialization/setup, table initialization, power up
* notificaiton ... ).
*
* @param task_id - the ID assigned by OSAL. This ID should be
* used to send messages and set timers.
*
* @return none
*/
void SimpleBLETest_Init( uint8 task_id )
{ //保存任务id到全局变量
SimpleBLETest_TaskID = task_id;
HalLcdWriteString ( "SimpleBLETest 1", HAL_LCD_LINE_1);
// Setup a delayed profile startup
/*
设置一个任务, 这么做的目的是按照多任务处理的方法来做
SimpleBLETest_ProcessEvent 就是处理 SBP_START_DEVICE_EVT
*/
osal_set_event( SimpleBLETest_TaskID, SBP_START_DEVICE_EVT );
}
/*********************************************************************
* @fn SimpleBLETest_ProcessEvent
*
* @brief Simple BLE Peripheral Application Task event processor. This function
* is called to process all events for the task. Events
* include timers, messages and any other user defined events.
*
* @param task_id - The OSAL assigned task ID.
* @param events - events to process. This is a bit map and can
* contain more than one event.
*
* @return events not processed
*/
// 这个是我们的应用程序的事件处理函数
uint16 SimpleBLETest_ProcessEvent( uint8 task_id, uint16 events )
{
VOID task_id; // OSAL required parameter that isn't used in this function
// SYS_EVENT_MSG 这是系统事件比如按键事件蓝牙读写事件处理,都会置这个事件
if ( events & SYS_EVENT_MSG )
{
// return unprocessed events
return (events ^ SYS_EVENT_MSG);
}
// 这个是我们应用程序自定义的事件,SBP_START_DEVICE_EVT 的值被定义为 0x0001,
// 实际上我们可以定义 16个事件, 第一的时候是以位来定义的
//
if ( events & SBP_START_DEVICE_EVT )
{
while(1)
HalLedSet(HAL_LED_1, HAL_LED_MODE_ON); // 点亮led1
// 返回这个, 告诉osal,这个事件你已经处理了
return ( events ^ SBP_START_DEVICE_EVT );
}
// Discard unknown events
return 0;
}
OSAL 的任务管理机制
OSAL 并不是我们已有概念的操作系统,但却是一个允许软件创建和执行时间的控制流程。OSAL 是整个操作系统的核心,BLE 协议栈,Profiles 特性,HAL 都是围绕在 OSAL 建立起来的,具体到代码来说,就是为每一层建立一个任务,协议栈里面各层的管理都是以任务处理的方式实现。
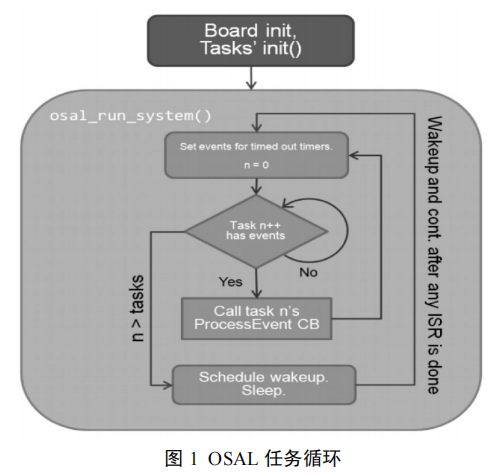
由上图可以看出,OSAL 就是一个死循环,不断循环检测是否有任务发生,如果有任务发生,则调用相应的任务处理函数,否则进入休眠进入下一次任务轮询。(该操作称为“心跳”)
低功耗原理
处理程序时,系统打开高速时钟,轮询所有任务是否有触发,轮询结束后,则切换到低速时钟,进行休眠,因为速度非常快,所以在每次“心跳”的大部分时间中,系统都处于休眠状态(例如工作0.05ms,休息0.95ms),平均下来功耗就非常小。
OSAL 事件处理机制
在 OSAL 中,事件十分重要,每个任务都有其事件列表,事件类型为 uint16,只有 16 个 bit,所以一个任务只能设置 16 个事件,我们把每一个 bit 称为事件标志(even_flag)。
和事件相关的处理函数:
// 到达指定时间后,调用事件
uint8 osal_start_timerEx( uint8 taskID, uint16 event_id, uint32 timeout_value );
// 立即调用事件
uint8 osal_set_event( uint8 task_id, uint16 event_flag );
OSAL 消息队列
事件是为了区分特定的事,同一事件的不同处理,应该使用消息队列来处理。OSAL 为消息建立一个动态分配内存的小系统。和消息相关函数调用如下:
// 申请内存
uint8 * osal_msg_allocate( uint16 len );
// 发送消息
uint8 osal_msg_send( uint8 destination_task, uint8 *msg_ptr );
// 接收消息
uint8 *osal_msg_receive( uint8 task_id );
// 释放内存
uint8 osal_msg_deallocate( uint8 *msg_ptr );
OSAL 回调机制
peripheralStateNotificationCB、simpleProfileChangeCB 分别是蓝牙状态变化和 profile 数据变化时调用的回调函数。
这些回调函数是系统在外部中断,状态中断上留下来的一些函数接口,允许用户添加处理函数到原来硬件或者协议栈中的一些状态变化。
参考
[1]郑海锐.浅析德仪OSAL工作原理[J].信息通信,2018,(05):288-289.
[2]OSAL操作系统-实验01 OSAL初探.pdf